Quantum Computing and Cloud Computing: A Symbiotic Journey
Quantum computing, an avant-garde branch of computing rooted in quantum theory, diverges significantly from classical computing’s reliance on binary digits (bits). While classical bits can only be in a state of 0 or 1, quantum bits, or qubits, exhibit the unique ability of superposition—simultaneously holding values of 0, 1, or any point in between.
Traditional supercomputers, once deemed the pinnacle of computational power, encounter challenges in certain scenarios, prompting the need for quantum computers. This article delves into the types of quantum computing systems and explores the intersection of quantum computing with cloud computing, unraveling their relationship and future prospects.
Types of Quantum Computers
- Quantum Circuit Model
- Quantum Turing Machine
- Quantum Adiabatic Computer
- Quantum Cellular Automata
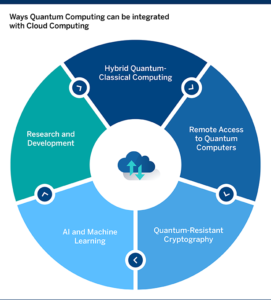
Quantum Computing in Cloud Computing
Defining the Synergy
Cloud computing, the delivery of diverse services such as data storage, servers, and databases via the internet, intertwines with quantum computing in the realm of cloud quantum computing. This amalgamation entails utilizing quantum computing capabilities over the internet. Cloud quantum computers, accessible remotely over the cloud, mark a paradigm shift in computational possibilities.
Leading companies like Google, Microsoft, IBM, and Amazon are not only champions of cloud computing but are also venturing into the development of cloud quantum computers. IBM currently leads the charge by offering cloud quantum computing access, with plans to expand services. This collaborative approach enables individuals to harness quantum computing power without possessing physical quantum computers, paving the way for widespread accessibility.
Relationship between Cloud Computing and Quantum Computing
Unlocking Mutual Potential
The relationship between cloud computing and quantum computing is symbiotic. Users lacking quantum computers can leverage cloud-based quantum computers, as major companies deploy their quantum machines on the cloud. IBM, a trailblazer in this domain, provides free access to its 5-qubit machine and recently introduced a 17-qubit quantum computer on the cloud. This collaborative synergy enhances the capabilities of both technologies.
The marriage of cloud computing and quantum computing opens avenues for decoding complex chemical structures, drug discovery, financial trading, risk management, and supply chain optimization. The secure handling of intricate data through more robust encryption becomes feasible, transforming the landscape of digital communication.
Applications of Cloud Quantum Computing
- Teaching: Quantum computing in the cloud facilitates teaching quantum physics, allowing students to comprehend concepts and conduct experiments without physical quantum computers.
- Research: Researchers can utilize cloud quantum computing for experiments, advancing quantum theories and contributing to the field’s evolution.
Future of Cloud Quantum Computing
Navigating Challenges and Envisioning Tomorrow
Martin Reynolds from Gartner emphasizes the complexities associated with implementing cloud-based quantum computing, highlighting a steeper learning curve compared to artificial intelligence. Quantum computing’s unique requirements demand specialized skills, posing challenges for IT teams accustomed to traditional digital programming approaches.
While the future of cloud quantum computing faces hurdles, its potential is vast. The technology, with its low I/O yet deep computation capabilities, aligns with cloud providers’ strengths. Overcoming practical challenges could position quantum cloud computing as pervasive as AI in the years to come, reshaping the landscape of computational possibilities.
FAQ
1. What sets quantum computing apart from classical computing, and how does it challenge traditional computational norms?
Answer: Quantum computing diverges from classical computing by employing quantum bits (qubits) that exhibit superposition—simultaneously representing 0, 1, or any value in between. This unique property challenges classical computing’s binary digit (bit) system, enabling quantum computers to perform complex calculations more efficiently.
2. How does cloud quantum computing redefine accessibility and utilization of quantum computing capabilities?
Answer: Cloud quantum computing involves accessing quantum computers over the internet, democratizing the use of quantum computing power. Leading companies like IBM provide cloud quantum computing access, allowing users to harness quantum capabilities without possessing physical quantum computers. This collaborative approach enhances accessibility and utilization.
3. What is the symbiotic relationship between cloud computing and quantum computing, and how does it benefit users?
Answer: Cloud computing and quantum computing share a symbiotic relationship where users lacking quantum computers can leverage cloud-based quantum computers. Major companies, exemplified by IBM, deploy quantum machines on the cloud, enhancing the capabilities of both technologies. This synergy benefits users by providing access to advanced computational power.
4. In what ways does the fusion of cloud computing and quantum computing transform various industries and applications?
Answer: The collaboration between cloud computing and quantum computing revolutionizes industries such as drug discovery, financial trading, risk management, and supply chain optimization. The secure handling of complex data through enhanced encryption reshapes digital communication, opening new possibilities for computational applications.
5. What challenges does the future of cloud quantum computing face, and how might it evolve in the coming years?
Answer: The implementation of cloud-based quantum computing poses challenges, including a steep learning curve and the need for specialized skills. Overcoming these hurdles is crucial for the technology’s evolution. Despite challenges, the potential of cloud quantum computing is immense, aligning with cloud providers’ strengths and paving the way for widespread adoption in the future.